Body shape is not just a matter of aesthetics; it plays a crucial role in determining our overall health and disease risk. Research has shown that different body shapes have distinct associations with various health outcomes. One such body shape that has garnered attention in recent years is the H2 body shape. In this blog, we will explore the correlation between body shape and disease risk, with a focus on H2 body shape. We will delve into the definition and characteristics of H2 body shape, its prevalence, and the factors influencing it. Additionally, we will examine the association between H2 body shape and diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and certain types of cancer. Finally, we will provide practical tips for managing H2 body shape and reducing disease risk.
Understanding Body Shapes and Health:
Definition of body shapes:
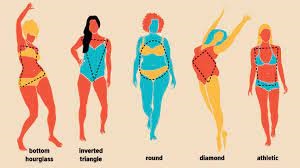
Body shapes can be broadly categorized into different types, including apple-shaped and pear-shaped bodies. Apple-shaped bodies have more fat accumulated in the abdominal region, while pear-shaped bodies have more fat distributed in the hips and thighs. It is important to note that body shape is not solely determined by fat distribution but also by overall body composition.
Understanding body shape is crucial as it can serve as an indicator of health outcomes. Research has consistently shown that body shape is associated with an increased risk of developing certain diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders.
Health risks associated with different body shapes:
Apple-shaped bodies: Individuals with apple-shaped bodies tend to have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke. The excess fat around the abdominal region, known as visceral fat, is metabolically active and releases inflammatory substances that can lead to insulin resistance, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipid levels.
Pear-shaped bodies: On the other hand, pear-shaped bodies have a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases compared to apple-shaped bodies. The fat stored in the hips and thighs is less metabolically active and has been associated with lower levels of inflammation and a healthier lipid profile. However, pear-shaped individuals may have an increased risk of certain metabolic disorders, such as osteoporosis.
Considering overall body composition and fat distribution is essential, as it provides a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health risks.
Introducing the H2 Body Shape:
A. Definition and characteristics of H2 body shape:
The H2 body shape refers to a distinct body type characterized by a more pronounced curvature in the upper body, specifically around the bust and shoulders, with a narrower waist and hips. Individuals with H2 body shape often have a well-defined hourglass figure, with a smaller waist-to-hip ratio.
Prevalence and factors influencing H2 body shape:
The prevalence of H2 body shape varies among populations and is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While genetics plays a significant role, lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity levels, and hormonal changes also contribute to the development of H2 body shape.
Correlation Between H2 Body Shape and Disease Risk:
Cardiovascular diseases:
Research suggests that individuals with H2 body shape may have a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases compared to apple-shaped individuals. The narrower waist-to-hip ratio observed in H2 body shape is associated with a healthier lipid profile, better insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation. However, it is important to note that other risk factors, such as smoking, high blood pressure, and unhealthy lifestyle habits, can still impact cardiovascular health.
Metabolic disorders:
H2 body shape is generally associated with a lower risk of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes. The distribution of fat in the lower body, particularly around the hips and thighs, is thought to be protective against insulin resistance. However, individual variations and other factors like age, genetics, and lifestyle choices can influence the overall metabolic health of individuals with H2 body shape.
Cancer risk:
The relationship between H2 body shape and cancer risk is an area of ongoing research. Some studies suggest that a higher waist-to-hip ratio, even within the H2 body shape category, may be associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including breast and colorectal cancer. The underlying biological mechanisms are complex and may involve hormonal factors and inflammation. Further research is needed to fully understand the correlation between H2 body shape and cancer risk.
Managing H2 Body Shape and Reducing Disease Risk:
Lifestyle modifications:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for individuals with H2 body shape to reduce the risk of developing diseases. This includes:
Engaging in regular physical activity, including both cardiovascular exercises and strength training.
Following a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or hobbies.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Medical interventions:
In some cases, medical interventions may be recommended to manage H2 body shape and associated health risks. These interventions may include:
Medications: In certain situations, healthcare professionals may prescribe medications to manage specific health conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Hormone therapy: For individuals experiencing hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy may be recommended under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Conclusion:
Understanding the correlation between body shape and disease risk, particularly in the context of H2 body shape, is crucial for promoting better health outcomes. While individuals with H2 body shape may have certain advantages, it is important to prioritize overall health by adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and seeking appropriate medical care. Ongoing research and advancements in the field of body shape and health will continue to shed light on the intricate relationship between body shape and disease risk, ultimately improving our ability to prevent and manage various health conditions.